Exploring REBA, RULA, and NIOSH Lifting Equation: Impact of AI on Workspace Optimization
This article provides an in-depth look at REBA, RULA, and NIOSH lifting equation assessments, explores the role of AI in enhancing ergonomic evaluations, and emphasizes the significance of ergonomic workstations for a healthy and productive work environment.
REBA (Rapid Entire Body Assessment)
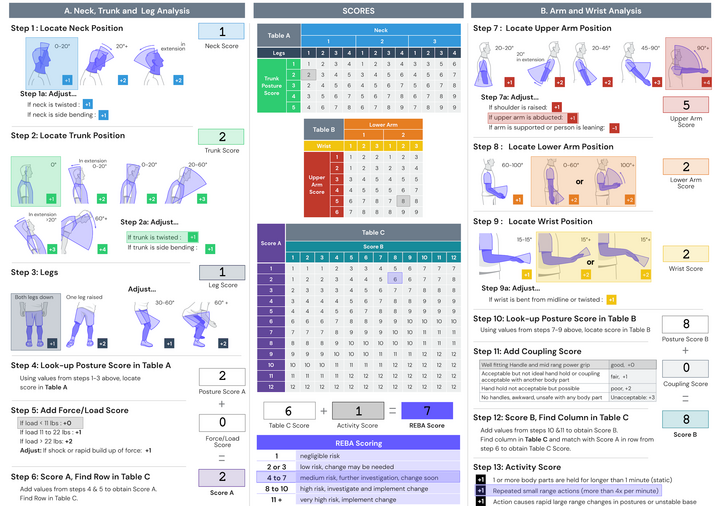
REBA is a systematic ergonomic assessment tool that evaluates whole-body postures to identify potential risks for MSDs. It considers a range of factors, including neck, trunk, leg, and arm positions, as well as the force exerted during specific tasks. By providing a comprehensive analysis of ergonomic hazards, REBA assists in identifying high-risk activities that require intervention and remediation. The tool assigns risk scores based on observed postures, allowing ergonomists to prioritize and implement appropriate measures to reduce the likelihood of work-related injuries and improve employee well-being.
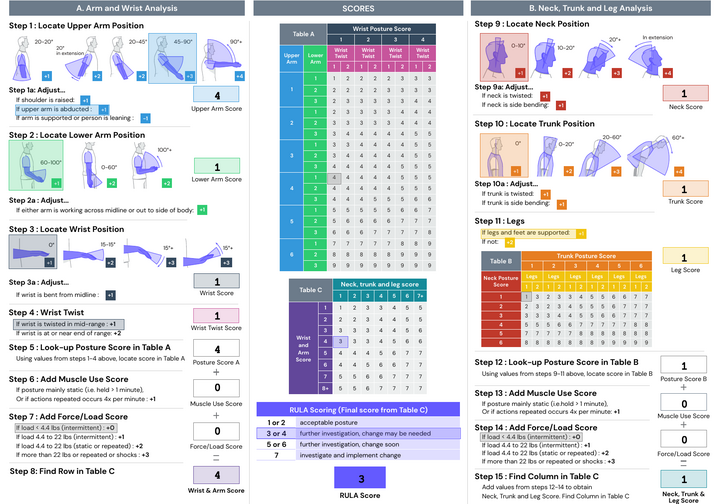
RULA (Rapid Upper Limb Assessment)

RULA focuses specifically on assessing the risks associated with repetitive tasks involving the upper body, including the arms, wrists, and hands. It assigns scores to various parts of the upper body based on posture and duration, enabling ergonomists to pinpoint areas of concern. RULA identifies tasks that contribute to awkward postures and repetitive motions, facilitating the implementation of corrective measures. By optimizing upper limb ergonomics, organizations can minimize strain on employees' musculoskeletal systems and reduce the risk of developing MSDs.
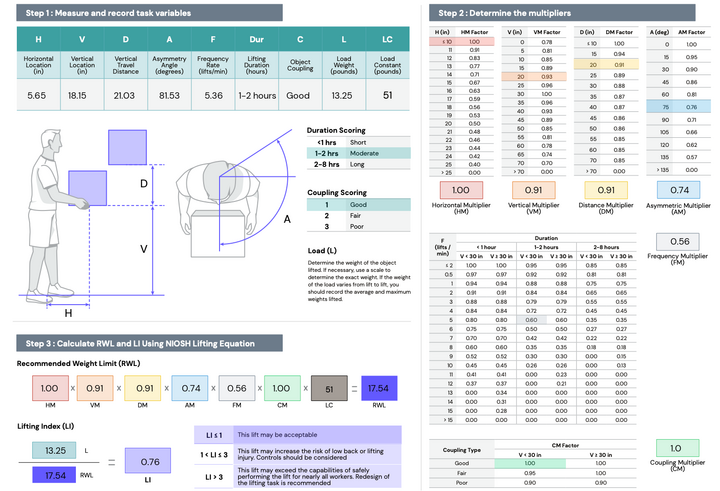
NIOSH Lifting Equation

The NIOSH lifting equation is a widely accepted tool for evaluating the risk of manual lifting tasks. It considers factors such as load weight, lifting technique, frequency, and duration to assess the stress placed on the body during lifting and lowering activities. By calculating a recommended weight limit and determining the lifting index, the NIOSH lifting equation helps employers determine whether a specific lifting task falls within acceptable ergonomic limits. Adhering to these guidelines enables organizations to protect their employees from injuries caused by excessive or improper lifting techniques.
The Role of AI in Ergonomic Assessments
Integrating AI has brought significant advancements to ergonomic assessments, enhancing accuracy, efficiency, and real-time feedback. AI algorithms can process and analyze large volumes of data, allowing for more precise recognition of patterns and postures, reducing subjectivity and potential errors associated with manual assessments.
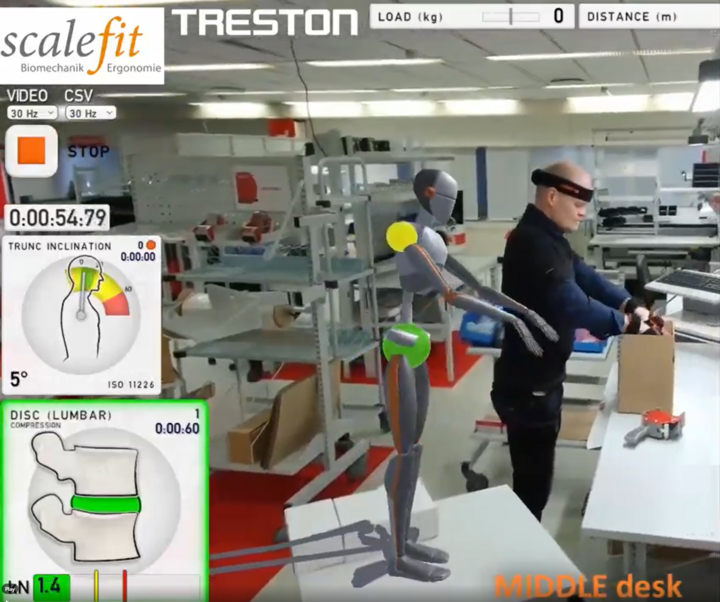
AI-powered ergonomic tools can leverage wearable devices and sensors to collect data on body movements, postures, and exertion levels. This real-time data can be analyzed and compared to established ergonomic guidelines, providing immediate feedback and interventions when necessary. AI algorithms can detect deviations from optimal postures, identify high-risk activities, and provide personalized recommendations for ergonomically sound practices. This proactive approach ensures a healthier and safer work environment for employees, reducing the risk of developing MSDs.

Camera-based assessment technology is another valuable tool. By using computer vision and AI, cameras can track employees' body movements and postures without the need for physical sensors. AI algorithms can then analyze the video footage in real-time, identifying ergonomic concerns like repetitive motions or awkward postures. This information can be used to provide personalized recommendations to employees or even trigger automated interventions, such as adjustable desks or reminders for stretching exercises.
The integration of AI in ergonomic assessments enables continuous monitoring and real-time feedback, ensuring proactive interventions to prevent workplace injuries. It also allows for the collection of large-scale data, which can be used to identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement across an organization. With the insights provided by AI, employers can implement targeted interventions, redesign workstations, and develop training programs to optimize ergonomics and promote a healthier and more productive work environment.
Prioritizing Ergonomics for a Healthy Workplace
REBA, RULA, and NIOSH lifting equation ergonomic assessments play a vital role in promoting workplace health and preventing occupational injuries. By identifying high-risk activities and implementing corrective measures, organizations can prioritize employee well-being and productivity.
Furthermore, the integration of AI has revolutionized ergonomic assessments, enabling more accurate and efficient evaluations. AI algorithms can process vast amounts of data, providing real-time feedback and personalized recommendations for improved ergonomics.

However, ergonomic assessments alone are not enough. Designing ergonomic workstations is crucial for creating a comfortable and productive work environment. By combining comprehensive ergonomic assessments, AI technology, and ergonomic workstations, companies can foster healthier work environments, reduce work-related injuries, and improve employee well-being, leading to increased productivity and overall satisfaction.
References:
RULA: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15676903/
REBA: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10711982/
NIOSH lifting equation: https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/docs/94-110/default.html