Are You Sitting Well? An Introduction to Proper Chair Ergonomics

Carissa Harris

What is the correct position for work, then? Ideally, a workstation should allow for workers to alternate between sitting and standing positions throughout their workday. Movement between positions exercises muscles and increases circulation, which energizes the body and mind. Studies show even slight movements, like standing up now and then, can improve memory, attentiveness, learning, and cognitive performance.
The solution to maintaining an ergonomic working position is pairing a height-adjustable table with a chair or stool that is suited to the worker and the work being done. A workplace chair must be an equally good fit for anyone, which is why it is essential to have a sufficiently wide range of settings and adjustments available.
Review these important chair features, positioning options, and recommendations for ordering the best office or industrial chairs for your workplace before requesting a quote from Treston.
Good Workplace Chair Features
-
Suitability for the measurements of the person/user – The goal is to first adjust the chair, not the person.
-
Supports the person in various working postures – Unsupported sitting in an upright posture results in 40% increase in disc pressure compared to standing. This may include a synchronous mechanism.
-
Promotes lumber lordosis – You want to utilize a backrest for the lower back and has a tilting seat.
-
Minimizes static loading of the back muscle – For example, using a reclined backrest can minimize static loading onto the back muscle.
-
Easy adjustability – An adjustable work seat promotes productivity and reduces pains in shoulders and in the back.

Recommended Workplace Chair Adjustments
It is not enough to simply pick a well-designed chair. A worker should also adjust the chair to fit their body and unique needs. Below are a few adjustment factors to consider when selecting a workplace chair:
- Seat Height – Allows adjustment to body size and height of workplace. The seat is at the correct height when the upper arms and forearms for a right angle and the forearms are level with the working surface. At the same time, the angle between the thighs and lower legs should be at least 90 degrees. The feet should be flat on the floor or on a footrest.
- Seat Tilt – Many jobs are carried out in slightly raised positions, and require people to bend forwards. A correspondingly tilted seat provides a seat angle of at least 90 degrees, while at the same time providing contact with the backrest. A forwards-tilting seat reduces the stress in the lower back. The seat should slightly be inclined forwards for jobs involving fine motor skills.
- Seat Depth – Matches the depth of the seat to the size of the body, giving the best possible contact surface for the thighs. The bottom should be right at the back of the seat to fit its anatomically shaped contours. Only this posture ensures a contact with the backrest so that the user benefits from its support. The front edge of the seat should be optimized for the length of the thighs, and not press against the lower limbs.
- Backrest Height – Ensures that a person is ideally supported – especially in the lumbar region – no matter how tall he/she is. Adjust the backrest so that its curvature supports the spine in the area of the 3rd and 4th lumbar vertebrae (approximately belt height).

Seat and backrest adjustment options. - Weight Regulation – By individually adjusting the pressure of the backrest, both light and heavy people can sit with the correct posture.
- Permanent Contact Backrest – It follows the movements of the upper body, and ensures that the back always remains fully supported. Ideal for people who must lean forward for long periods of time, with only a small distance between eyes and workplace (e.g. working in precision engineering or in the laboratory).
- Synchronous mechanism – This provides an active-dynamic sitting experience with weight regulation. The seat and backrest accompany to body as it moves. This gives the user a feeling that can best be described as “weightless floating”. The synchronous technology comes into its own where users are working at office type working situations, working at a screen, or constantly changing their sitting position.
- Armrests – Armrests have the important function of reducing the strain on the upper body and arms. The height, and width of 3D armrests can be adjusted, and can also be swiveled. In addition, armrests can feature depth adjustment. Upper arms should be close to the body, shoulders relaxed, and forearms should rest naturally.
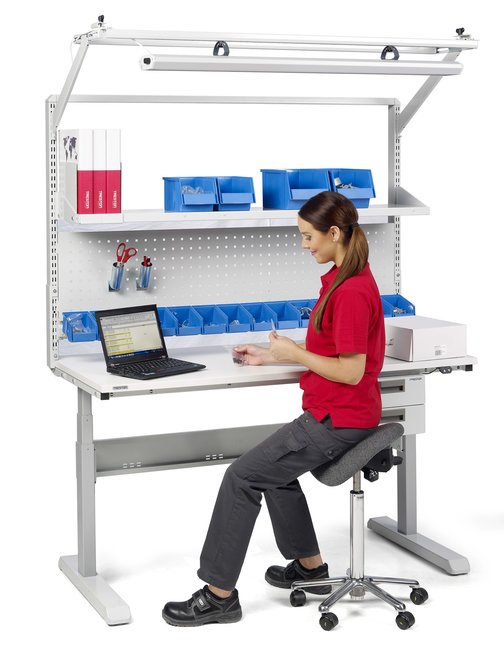


How to Choose a Sitting or Standing Work Position
Latest cognitive research shows how beneficial changing working posture can be.If tasks require paperwork, typing, no heavy lifting, and/or all tools for the job are provided in arm’s reach, then the workstation should be designed primarily for sitting, but with the possibility to stand still available.
If tasks require lifting heavy loads, continuous movement, parts retrieval, with minimal leg space, then the workstation should be designed for standing, but with the possibility to rest when possible. Even though stand-up working posture is becoming increasingly popular, many official recommendations still state that proper seating ergonomics is one of the most crucial aspects of preventive actions for work related musculoskeletal disorders. It is not indifferent how or on what you are sitting!
There is also a third position to consider. Semi-sitting is a position between standing and sitting that allows a worker to stand for prolonged periods with no signs of fatigue by supporting a person’s posture without forcing them into a position. Standing rest takes off 60% of your body weight from your feet compared to standing. Using a work stool or a saddle chair creates a 135-degree angle between the thighs and the upper body, which improves blood circulation in the hip and knee joints.
Not sure which style chair is ideal for your working environment? Below are two charts to help you decide.


Choosing the Right Workplace Chair
Finally, it is important to remember safety when selecting a workplace chair. Here are some tips to consider:
- A chair over 25.5” needs to have glides and a foot ring to create a safe sitting position.
- “Stop and Go” casters are a good option when a chair will be moved out of the workspace when not in use. The stopping mechanism on these casters ensures the chair will not move when the worker is sitting. It can also prevent movement during sensitive work.
- ESD chairs are available when working with sensitive parts or equipment.
- Seat material can be just as important as seat adjustment. When choosing a semi-sitting stool, for example, consider a slip-resistant material.
- Industry standard dictates a chair should conform to the DIN 68 877 requirements. Be sure to look for the GS safety mark when selecting a chair.
Find Your Next Work Chair from Treston Today
No matter the work being done, a workplace can benefit from varying working positions. When seeking potential work chairs and solutions, be sure to consider standing rests, saddle chairs, footrests, chair accessories, and easily adjustable workbenches, which allow for both sitting and standing work that may be most suitable for your environment and staff. A comfortable employee is a happy and productive employee!
Contact the Treston team with questions you may have about ergonomic chairs, and customize your entire workplace, including chairs, with our online 3D Configurator Tool today!
Sources:
http://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/adult-health/expert-answers/sitting/faq-20058005
https://www.ccohs.ca/oshanswers/ergonomics/standing/standing_basic.html